Artificial intelligence (AI) has quickly become part of everyday life. From AI assistants in smartphones to biometric recognition tools that secure our finances, intelligent systems now shape how we live, work and communicate. In fact, AI has even made impressive strides in transforming the healthcare landscape.
Across the medical field, AI technologies help healthcare professionals analyze complex data, make faster clinical decisions and improve patient outcomes. What once sounded like science fiction, such as AI-enabled robots assisting in surgery or virtual health assistants supporting patient care, is now a growing part of everyday medicine.
The rise of AI in healthcare reflects a major shift in how medical professionals approach care delivery. Faced with rising costs, data overload and the growing demand for precision medicine, the healthcare system is turning to AI to fill critical gaps and increase efficiency. AI systems can process vast amounts of health data from medical records, wearable devices and diagnostic tools, offering insights that might otherwise go unnoticed.
As AI in medicine continues to evolve, it’s becoming clear that this technology is redefining what’s possible in healthcare collaboration. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how AI is used in healthcare, highlighting its key applications, benefits and challenges. You’ll also learn how healthcare professionals, researchers and educators are preparing for an AI-driven future where technology and human expertise work side by side to deliver better care for all.
The Dawn of AI in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence refers to the ability of machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning and problem-solving. In healthcare, AI technologies rely heavily on machine learning, a branch of AI that enables systems to learn from data and improve performance over time without explicit programming. This allows computers to recognize patterns, make predictions and even assist in clinical decisions that affect patient care.
The Growing Need for AI in Healthcare
The demand for AI in healthcare has been driven by multiple forces reshaping the industry. For instance, rising operational costs, physician shortages and an explosion of medical data have all made traditional systems increasingly difficult to sustain. Healthcare organizations now face the challenge of doing more with less. In essence, they are tasked with delivering efficient, high-quality care while managing vast amounts of information.
AI systems help close that gap. By processing large datasets faster than humans ever could, they enable healthcare professionals to detect diseases earlier, personalize treatments and streamline administrative tasks. The result is a healthcare system that’s more responsive, data-driven and patient-centered.
How Is AI Used in Healthcare?
The applications of AI in healthcare are expanding rapidly. From diagnostics to drug development, AI tools are reshaping nearly every stage of patient care. Hospitals and research institutions around the world are integrating AI-enabled systems into daily operations to significantly improve efficiency and accuracy.
In hospitals, AI assists clinicians by reviewing medical records, identifying risk factors and suggesting optimal treatment options. Clinics additionally use AI chatbots and virtual health assistants to improve patient experiences, while research centers leverage AI for analyzing medical data to accelerate discoveries. Compared to traditional healthcare methods, AI’s speed and precision often result in more accurate diagnoses and more personalized patient care.
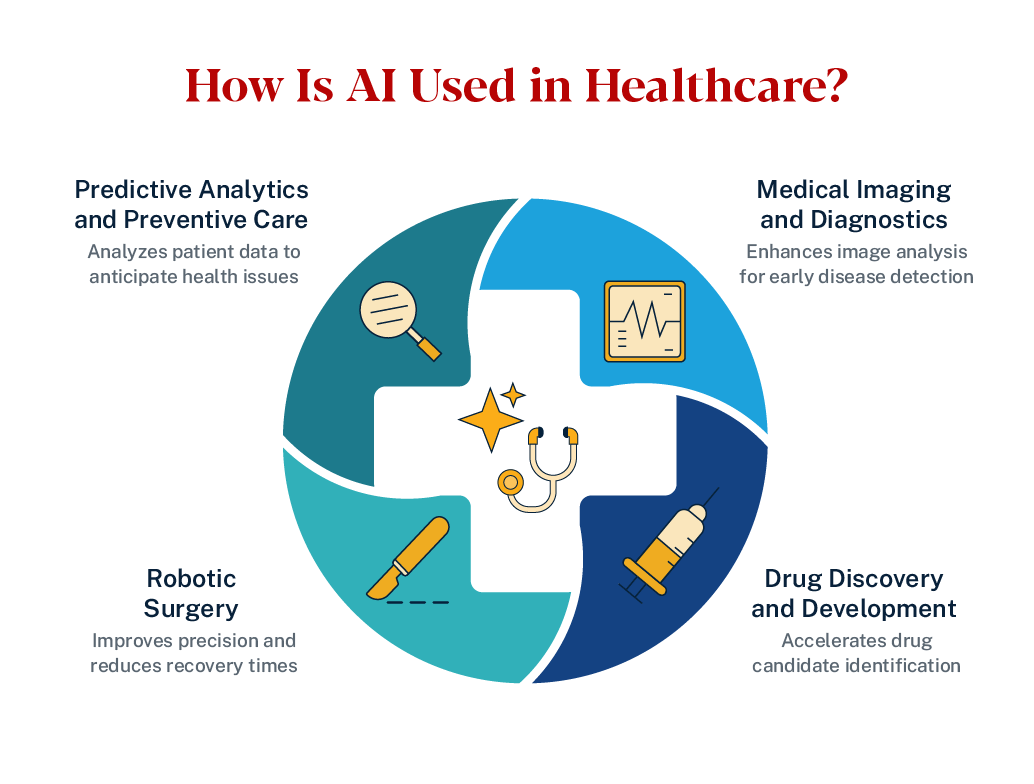
AI in Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
Medical imaging has become one of the most promising areas for AI innovation. Algorithms can analyze X-rays, CT scans and MRIs to identify anomalies such as tumors, fractures or internal bleeding with remarkable accuracy. These systems act as a second set of eyes, supporting radiologists in detecting patterns that may be too subtle for human observation.
Another example is in pathology. AI helps process digital slides to identify cancerous cells or other diseases faster and with greater precision. Studies show that combining human expertise with AI analysis improves diagnostic accuracy and reduces error rates, contributing to better patient outcomes.
AI in Drug Discovery and Development
Drug discovery has traditionally been a time-consuming and expensive process, often taking years of research and billions of dollars to bring a single drug to market. As it happens, AI is helping change that.
By analyzing vast datasets from medical research, AI tools can identify potential drug candidates more efficiently and predict their efficacy. This not only accelerates early-stage research but also reduces costs and improves safety.
AI also plays a critical role in clinical trials. By using its algorithms, researchers can identify suitable participants based on genetic markers or medical history and analyze trial results in real time. This level of precision accelerates the drug development process while maintaining high standards of scientific integrity.
AI in Predictive Analytics and Preventive Care
AI’s ability to analyze large volumes of data makes it an invaluable tool for predictive analytics. By assessing patient records, genetics and lifestyle information, AI models can predict an individual’s risk of developing certain conditions before symptoms appear.
These predictive tools support healthcare professionals in developing personalized treatment plans and preventive care strategies. For example, genetic analysis powered by AI can help identify patients more likely to develop heart disease or diabetes, allowing for early intervention. Predictive analytics also extend to population health management, helping healthcare organizations allocate resources more effectively and reduce long-term costs.
AI in Robotic Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery is one of the most visible examples of AI in medicine. These systems enable surgeons to perform highly precise and minimally invasive procedures. AI enhances robotic control systems by interpreting visual data and making real-time adjustments during surgery, increasing accuracy and reducing risk.
After surgery, AI continues to play a role through tools that monitor recovery progress and predict potential complications. This combination of precision and proactive care helps improve outcomes and shorten recovery times for patients.
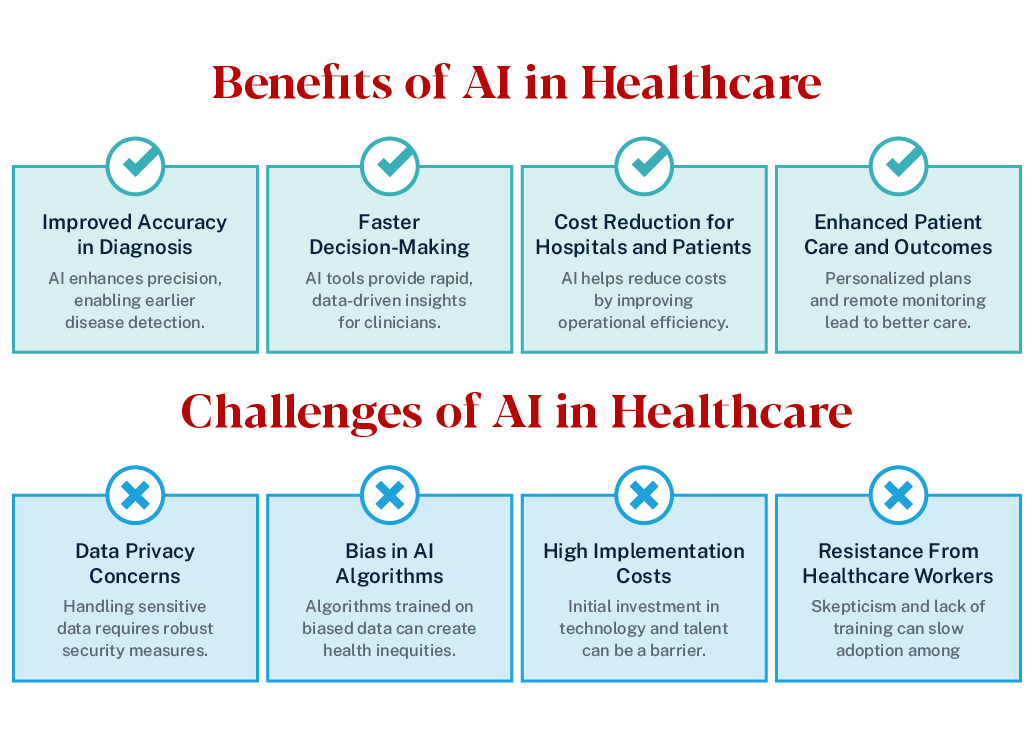
Benefits of AI in Healthcare
The growing adoption of AI in healthcare is driven by its many advantages. To understand why hospitals, clinics and research institutions are investing in these technologies, it’s helpful to look at the benefits of AI in medicine.
- Improved diagnostic accuracy: AI models can detect diseases earlier and with greater precision than traditional methods, reducing the risk of misdiagnosis.
- Faster decision-making: Clinicians can make timely, informed decisions with the support of AI tools that analyze data instantly.
- Cost reduction: AI streamlines administrative and clinical workflows, reducing costs for both hospitals and patients.
- Enhanced patient outcomes: Personalized care plans and predictive analytics help prevent complications and improve long-term health.
These benefits demonstrate how AI supports not just clinicians but entire healthcare systems, creating a more sustainable and equitable model of care.
Challenges of AI in Healthcare
Despite its promise, implementing AI in healthcare comes with challenges that must be addressed carefully. Understanding these limitations is essential to ensure safe, ethical and equitable AI adoption.
- Data privacy concerns: Protecting patient information remains a top priority under laws such as HIPAA and GDPR. AI tools must meet strict data security standards to safeguard sensitive health data.
- Bias in AI algorithms: AI systems learn from existing data, which can contain unintentional biases. If not managed properly, these biases may lead to inequitable care or inaccurate results.
- High implementation costs: Developing and integrating AI systems requires significant investment in infrastructure, training and maintenance.
- Resistance from healthcare workers: Some professionals are hesitant to adopt AI, fearing job displacement or overreliance on technology.
Addressing these challenges will require collaboration between healthcare providers, policymakers and educators to ensure AI is implemented ethically and effectively.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
As AI continues to evolve, its potential in healthcare is expected to see outstanding growth. Future advancements will likely focus on making it more accessible, inclusive and integrated into everyday medical practice.
One promising development is the use of AI in rural and underserved areas, where access to healthcare professionals is limited. AI-powered diagnostic tools and telemedicine platforms can bring expert-level analysis to remote locations, helping close the gap in healthcare equity.
Integration with wearable devices is another growing trend. Smartwatches and health trackers collect continuous streams of data that AI can analyze to detect irregularities or alert patients to potential health issues before they become critical.
Ultimately, the goal is to build a strong human-AI partnership. Rather than replacing clinicians, AI will act as a supportive partner that helps doctors make more informed decisions and improve collaboration across healthcare teams. As the technology matures, this partnership promises to create a system where efficiency, empathy and precision coexist.
Case Studies of AI in Healthcare
The best way to understand how AI is transforming medicine is to look at real-world examples. Across hospitals, research centers and private companies, AI systems are already being used to support physicians, analyze medical data and improve patient outcomes.
Several initiatives stand out for their measurable impact on healthcare delivery.
- IBM Watson for Oncology
- IBM Watson for Oncology was among the earliest large-scale efforts to apply artificial intelligence in medicine. The system is designed to assist oncologists by analyzing vast amounts of medical records, clinical trial data and scientific literature to recommend personalized treatment options. By comparing a patient’s unique health data to thousands of medical studies, Watson can identify therapies that are most likely to be effective based on evidence and similar cases.
Hospitals using the system have reported improved treatment planning efficiency and stronger adherence to clinical guidelines. While Watson has faced some criticism regarding complexity and data integration, it remains a major example of how AI technologies can help physicians manage the overwhelming volume of available research and support more evidence-based care.
- IBM Watson for Oncology was among the earliest large-scale efforts to apply artificial intelligence in medicine. The system is designed to assist oncologists by analyzing vast amounts of medical records, clinical trial data and scientific literature to recommend personalized treatment options. By comparing a patient’s unique health data to thousands of medical studies, Watson can identify therapies that are most likely to be effective based on evidence and similar cases.
- Google DeepMind
- Google’s DeepMind Health initiative demonstrates how AI can elevate diagnostic accuracy to new levels. One of its most successful collaborations, with Moorfields Eye Hospital in London, focused on detecting retinal diseases through deep learning models. The AI system was trained using thousands of retinal scans and achieved diagnostic accuracy comparable to expert ophthalmologists.
In addition to identifying conditions such as diabetic retinopathy and macular degeneration, the system could also recommend the urgency of patient referrals, helping doctors prioritize cases and prevent vision loss. DeepMind’s research has since expanded into other areas, including breast cancer screening and patient outcome prediction, reinforcing AI’s potential to augment clinical expertise and reduce diagnostic delays.
- Google’s DeepMind Health initiative demonstrates how AI can elevate diagnostic accuracy to new levels. One of its most successful collaborations, with Moorfields Eye Hospital in London, focused on detecting retinal diseases through deep learning models. The AI system was trained using thousands of retinal scans and achieved diagnostic accuracy comparable to expert ophthalmologists.
- Mayo Clinic AI Initiatives
- The Mayo Clinic has become a leader in implementing healthcare AI applications that span across radiology, cardiology and patient monitoring. One key innovation is the use of predictive analytics powered by AI models that analyze patient data to forecast health risks, such as the likelihood of cardiac arrest or sepsis. These insights allow medical teams to intervene earlier and improve patient survival rates.
The clinic also uses AI tools to interpret imaging scans more efficiently, shortening wait times for diagnosis and reducing physician workload. Their partnership with Google Cloud has enhanced their ability to securely process health data, paving the way for future AI-driven collaboration and medical research.
- The Mayo Clinic has become a leader in implementing healthcare AI applications that span across radiology, cardiology and patient monitoring. One key innovation is the use of predictive analytics powered by AI models that analyze patient data to forecast health risks, such as the likelihood of cardiac arrest or sepsis. These insights allow medical teams to intervene earlier and improve patient survival rates.
These examples highlight the growing confidence in AI’s ability to support medical professionals and accelerate innovation. Each project reinforces how artificial intelligence can help healthcare systems become more precise, efficient and responsive to patient needs.
FAQs About AI in Healthcare
Will AI replace doctors?
No. AI is designed to assist doctors, not replace them. It enhances efficiency and accuracy while allowing clinicians to focus on patient care and complex decision-making.
How accurate is AI in medical diagnosis?
AI diagnosis accuracy varies by application, but it has shown exceptional performance in areas such as radiology and pathology, often matching or exceeding human-level precision when used as a complementary tool.
Is AI in healthcare safe?
Yes, when properly regulated and monitored. AI systems undergo rigorous testing to ensure compliance with safety and privacy standards.
What is the most common use of AI in medicine?
AI is most widely used in medical imaging, diagnostics and administrative automation. These applications help improve accuracy, reduce workload and streamline hospital operations.
Learn, Innovate and Shape the Movement Shaping Healthcare’s Future
AI is actively redefining how healthcare is delivered, managed and experienced. From supporting doctors in clinical decisions to improving diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes, AI is helping create a more connected and efficient healthcare system. Yet for this progress to continue, the field needs professionals who understand how to use technology responsibly and effectively.
Artificial intelligence may be reshaping medicine, but you can be the human element that remains at its core. By combining advanced education with the possibilities AI has to offer, you can help build a smarter, more equitable and more compassionate system of care.
American College of Education is committed to integrating AI in its coursework. We offer innovative, relevant programs that support healthcare professionals and nurses with the tools they need to succeed in today’s AI-driven healthcare landscape.

